Stepper motors, which offer exact control over positioning and speed, are crucial parts of many industrial applications. Three popular types of stepper motors—Geared, Hybrid, and Permanent Magnet (PM)—each come with distinct features that make them suitable for different uses.
This article will explore the strengths and weaknesses of these three motor types, helping you determine which one is the best fit for your specific industrial needs.
Overview of Stepper Motors
It’s critical to comprehend the fundamental operation of a stepper motor before delving into the particulars of each type. Electrical pulses are transformed into distinct mechanical movements by stepper motors.
Stepper motors provide excellent accuracy and repeatability by moving in exact steps as opposed to conventional motors, which rotate continuously. This makes them perfect for applications like industrial automation, robotics, and CNC machines that need exact control over movement.
Geared Stepper Motors
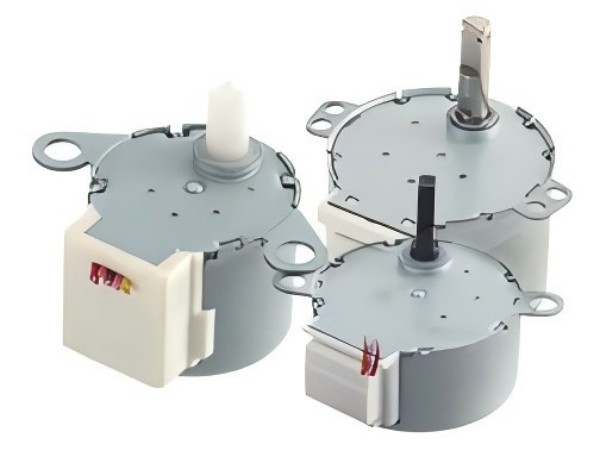

In essence, geared stepper motors are stepper motors with a gear system added, which lowers the motor’s speed while raising its torque.
When a high torque at low speeds is needed, these motors are perfect. By coupling a stepper motor with a gear system, the output torque can be significantly enhanced without requiring a larger motor.
Key Advantages:
- High Torque at Low Speeds: They are appropriate for heavy-duty applications because of the gear reduction, which boosts torque.
- Precise Control: The stepper motor’s inherent ability to control position is retained, and the gear mechanism allows for even more precise control over movement.
- Compact Design: Geared stepper motors combine the compactness of stepper motors with the added benefit of increased power, making them ideal for space-constrained applications.
Key Disadvantages:
- Added Complexity: The mechanical intricacy of a gear system may result in increased maintenance needs.
- Reduced Efficiency: The mechanical gears introduce additional friction, which can reduce overall efficiency and increase wear over time.
- Higher Noise Levels: The gears can generate noise, which may be undesirable in certain applications.
Geared stepper motors are commonly used in robotics, conveyors, and other applications where high torque is necessary but space is limited.
Hybrid Stepper Motors
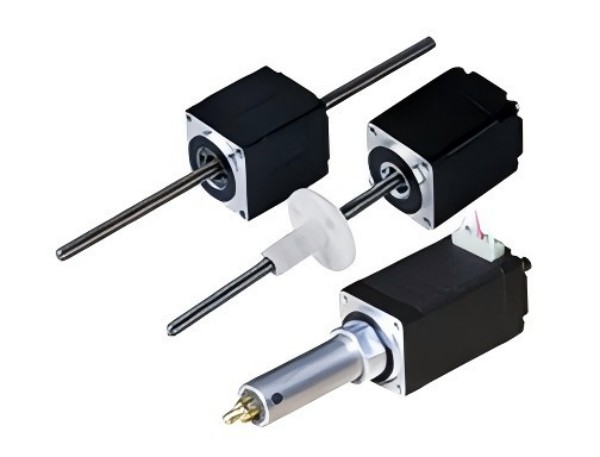

The best qualities of both variable resistance and permanent magnet stepper motors are combined in hybrid stepper motors. They provide a more efficient solution compared to traditional stepper motors by offering both high torque and precision control. The hybrid design allows for better performance, particularly at higher speeds.
Key Advantages:
- Higher Efficiency: The hybrid design offers better efficiency than traditional PM or VR stepper motors.
- Precision and Torque: Hybrid stepper motors provide excellent precision while maintaining good torque at higher speeds.
- Cost-Effective: They are popular for a variety of applications because they provide a good balance between cost and performance.
Key Disadvantages:
- Complex Design: Hybrid motors are more complex than simple PM or VR motors, which can lead to higher costs and more complicated maintenance.
- Higher Heat Generation: These motors tend to generate more heat than other stepper motor types, requiring effective cooling solutions.
For precise devices that need both high torque and fast speed, such as CNC machines and 3D printers, hybrid stepper motors are frequently utilized.
Permanent Magnet (PM) Stepper Motors
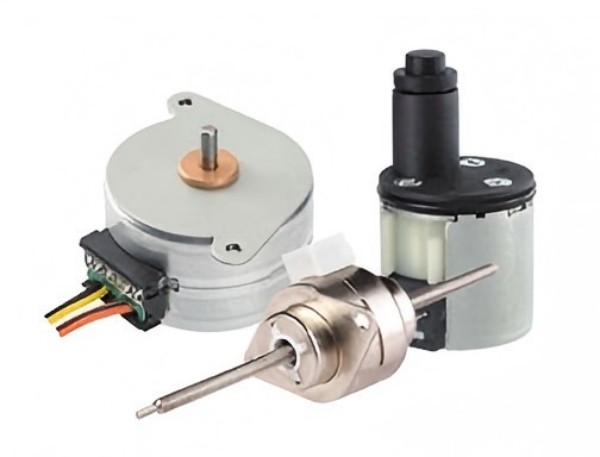

Permanent Magnet stepper motors use a permanent magnet in their rotor, which interacts with the stator’s magnetic field to produce movement. Compared to geared stepper motors and hybrid stepper motors, these motors are typically easier to build, which lowers their cost in many applications.
Key Advantages:
- Cost-Effective: The simple design makes PM stepper motors less expensive than other types.
- Compact and Lightweight: Because these motors are usually lighter and smaller, they are appropriate for portable applications.
- Lower Power Consumption: PM stepper motors are more energy-efficient than some hybrid designs, particularly for lower-torque applications.
Key Disadvantages:
- Reduced Torque at High Speeds: PM stepper motors’ employment in high-speed applications is restricted by their propensity to operate poorly at higher speeds.
- Lower Precision: While they provide good precision at lower speeds, they lack the accuracy and torque capabilities of hybrid or geared stepper motors at higher speeds.
PM stepper motors are commonly used in small-scale applications such as printers, low-power automation systems, and small machinery.
Comparative Table: Geared vs. Hybrid vs. PM Stepper Motors
| Feature | Geared Stepper Motors | Hybrid Stepper Motors | Permanent Magnet Stepper Motors |
| Torque | High at low speeds | Moderate to high across a range of speeds | Low at high speeds |
| Speed | Low speed, high torque | High speed and torque at a balanced level | Low to moderate speed, limited at high RPM |
| Precision | High precision, excellent for low-speed control | Excellent precision and torque across speeds | Good precision at low speeds |
| Efficiency | Lower due to gears | Higher than PM motors | Good efficiency at low speeds |
| Cost | Higher due to mechanical complexity | Mid-range cost, cost-effective for many tasks | Most cost-effective |
| Maintenance | Higher due to gears | Moderate, but higher than PM motors | Lower, simple design |
| Application | Robotics, conveyors, heavy-duty tasks | CNC machines, 3D printers, precise control | Printers, small-scale automation |
Choosing the Right Stepper Motor
A geared, hybrid, or PM stepper motor will be selected based on the particular needs of your industrial application.
- Geared Stepper Motors: Best suited for tasks that demand high torque at low speeds, including robotics and conveyors. These motors excel in environments where space and power are limited.
- Hybrid Stepper Motors: Best for applications requiring both high speed and high torque, such as CNC machines and 3D printers. They provide a cost-effective and performance-balanced solution.
- Permanent Magnet Stepper Motors: Perfect for low-cost, small-scale applications where high precision and energy efficiency are key, such as printers or small machines.
Conclusion
Geared stepper motors are great for high-torque, low-speed applications, while hybrid stepper motors provide excellent balance for precision and speed. Permanent magnet stepper motors are ideal for cost-sensitive applications where simplicity and efficiency are the priority.
When selecting a stepper motor for your industrial needs, consider the specific requirements of your application—whether it’s torque, speed, precision, or cost—and choose the motor type that best fits these needs.

