Stepper Motor Manufacturer
Our stepper motors are available in customizable sizes and form factors, providing versatile solutions tailored to meet industry-specific needs.
Designed for high precision, high torque, and durability, they ensure optimal performance in compact systems, automation, robotics, and more.
- Various Types: Hybrid, PM, VR, Synchronous
- Voltage Range: 3V~48V
- Step Angle Range: 0.9°~18°
- Phases Number: From single to multi-phase configurations
- Special Features: Variable speed, Explosion-proof, waterproof, silent
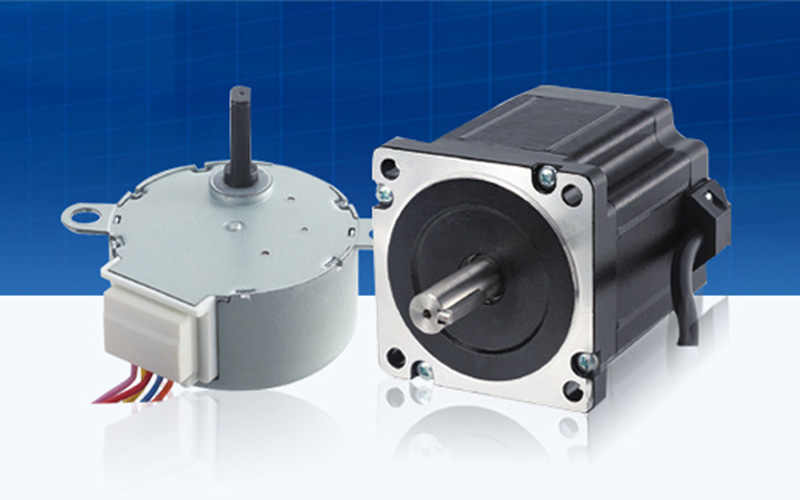

What Types of Stepper Motor Can We Provide?
Our stepper motors come in various types: Hybrid, Permanent Magnet (PM), Variable Reluctance (VR), Synchronous, each with specific applications.
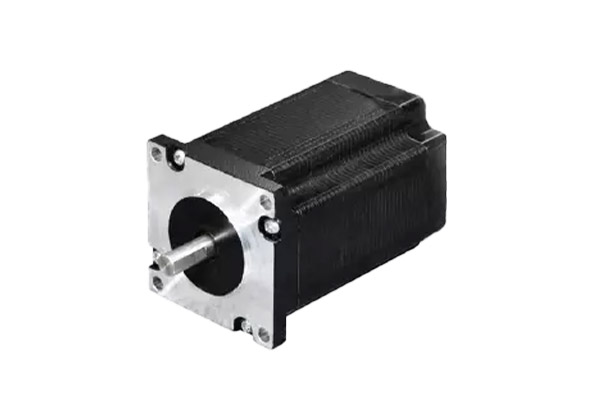

Hybrid Stepper Motor
- Fuses permanent magnet and variable reluctance designs.
- Provides high torque and precise positioning.
- Step Angle: 0.9° to 1.8°, high accuracy.
- Used in CCTV monitor, medical appliance, OA finance, industrial equipment.
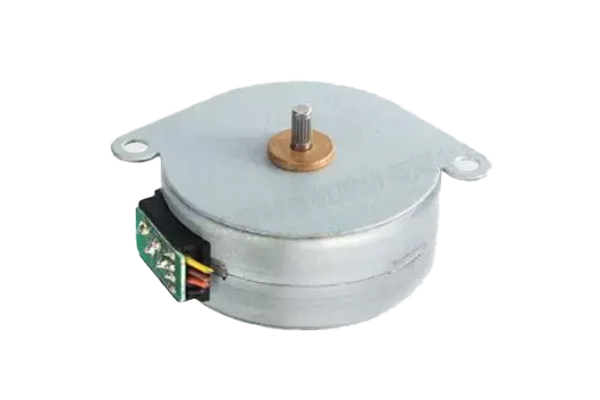

Permanent Magnet Stepper Motor (PM)
- Uses permanent magnets for rotor construction.
- Offers smoother operation with lower noise levels.
- Step Angle: 7.5° to 18°, moderate torque.
- Used in OA finance, valve control, security monitoring, auto parts.
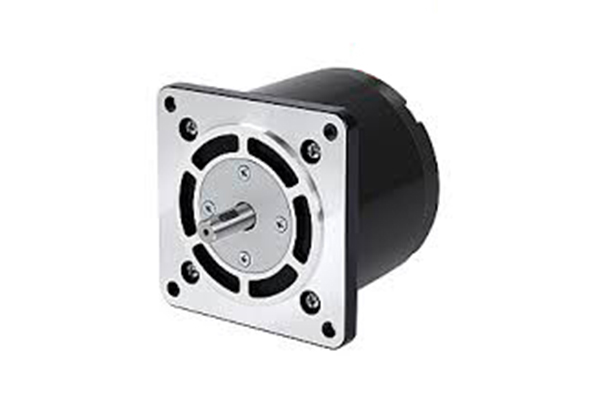

Variable Reluctance Stepper Motor (VR)
- Rotor is formed of a soft iron core.
- Cost-effective but lower torque output.
- Step Angle: 5° to 15°, higher step resolution.
- Used in robotics, conveyor systems, and printers.

Synchronous Stepper Motor
- The rotor synchronizes with the stator field.
- Provides constant speed with minimal loss.
- Step Angle: 0.9° to 15°, consistent rotation.
- Applied in clock mechanisms, industrial automation, and robotics.
What Can Our Stepper Motor Combine With?
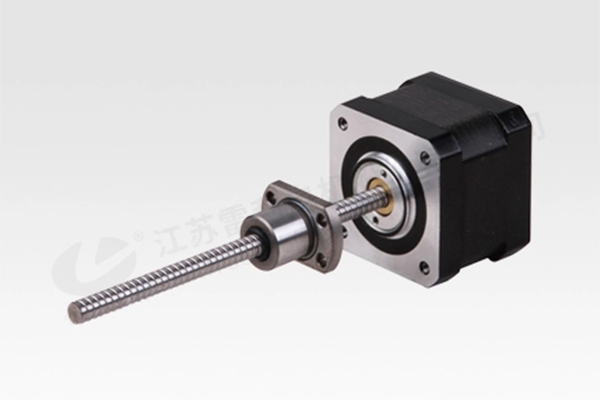

linear Motion Actuators
- Our stepper motors integrate with linear motion actuators to deliver precise, controlled linear movement. This combination is perfect for applications like 3D printing, robotics, and automated systems that require accurate positioning and repeatability.
- Voltage Range: 6.6V
- Size: 32*14.3*11.8mm
- Lead Screw Length: 1.5 ± 0.2 mm
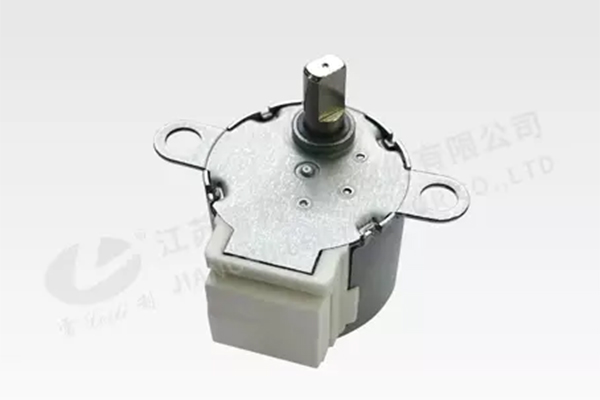

Gearbox Devices
- When paired with gearbox devices, our geared stepping motors provide increased torque and reduced speed. This combination is ideal for applications requiring high power, and precise control, such as air conditioners, refrigerators, smart toilets, auto parts, and security monitoring.
- Voltage Range: 5V, 12V, 24V
- Step Angle: 3.75°, 5.625°,7.5°
- Noise: ≤40dB(A)
Based on Drive Methods
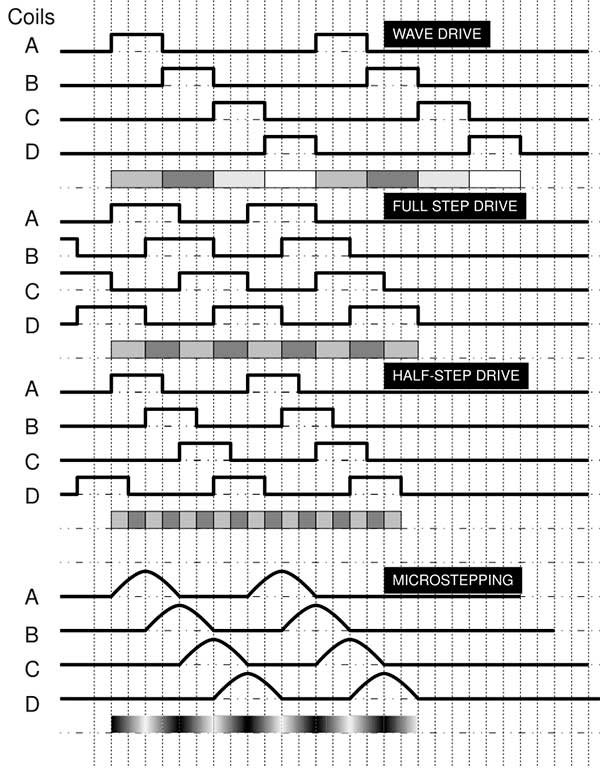
Stepper motors offer various drive methods, including full-step, half-step, wave drive, and microstepping, each balancing precision, torque, and efficiency.
Full-step Drive
- Step Angle: 1.8° or 0.9° per step.
- Provides maximum torque at each step.
- Simple control, but more vibration and noise at lower speeds.
Half-step Drive
- Step Angle: 0.9° or 0.45° per step.
- Smoother motion compared to full-step drive.
- Reduces vibrations and increases precision at a moderate speed.
Wave Drive
- Step Angle: 1.8° or 0.9° per step.
- Energizes one coil at a time, reducing power consumption.
- Lower torque output compared to full-step and half-step drives.
Microstepping
- Step Angle: 0.1° to 0.05° per microstep.
- Provides smooth motion and reduces noise and vibrations.
- Increased precision, but torque output is lower than other methods.
Based on Voltage Ratings
Stepper motors are available in low, medium, and high voltage ratings, catering to various power needs and performance requirements.
Low Voltage
- 3V, 5V, 6V Stepper Motors.
- Suitable for low-power applications with precise control.
- Efficient and ideal for small devices or equipment.
Medium Voltage
- 12V, 24V Stepper Motors.
- Best for moderate power requirements and medium-sized equipment.
- Provides stable performance and reliability in various uses.
High Voltage
- 48V Stepper Motor.
- Designed for high-power, high-performance industrial applications.
- Delivers smooth operation for demanding applications.
Based on Phases Number
Stepper motors come in single-phase to multi-phase configurations, offering varying levels of torque, precision, and smoother operation for diverse applications.
Single Phase
- One winding for a simple, basic design.
- Low phase count results in lower torque output.
- Suitable for low-power and cost-effective setups.
2-Phase
- Two windings placed 90° apart for balanced performance.
- Provides higher torque compared to single-phase motors.
- Common design with standard control for versatility.
3-Phase
- Three windings separated by 120° for smoother motion.
- Delivers more torque and efficiency than 2-phase motors.
- Offers better overall stability and performance.
4-Phase
- Four windings spaced 90° apart for increased precision.
- Higher resolution and torque compared to 2-phase motors.
- More complex windings provide smoother operation.
5-Phase
- Features five windings for finely tuned control.
- Smaller step angles, offering high precision and smoothness.
- Reduces noise and vibration during operation.
Variable Phase
- Combines different phase configurations for flexibility.
- Offers adjustable windings for optimized phase control.
- Provides variable torque&precision for diverse uses.
Based on Polarity
Stepper motors operate as unipolar or bipolar, offering simpler circuitry for unipolar, and higher torque with bipolar configurations.
Unipolar
- Has a common center tap for each coil phase.
- Current passes in one direction through each coil.
- Simpler drive circuitry with less complex polarity control.
Bipolar
- No center tap; current flows in both directions.
- Requires more complex drive circuitry for polarity reversal.
- Delivers higher torque by using both coil polarities.
Based on Winding Configuration
Stepper motors come in various winding configurations, including 2-wire to 8-wire setups, offering flexibility, precision, and control for different applications.
2 Wire
- Simple, basic two-wire control setup.
- Low-power applications, compact design.
- Easy to interface with basic controllers.
3 Wire
- Adds a common wire for flexibility.
- Suitable for moderate power applications.
- Provides more stable control than 2-wire motors.
4 Wire
- Bipolar coil configuration for higher precision.
- Offers improved torque and control.
- Ideal for systems requiring accurate movement.
5 Wire
- Extra wire for enhanced control flexibility.
- Often used in unipolar motor configurations.
- Reduces noise and improves movement precision.
6 Wire
- Can be used in unipolar or bipolar configurations.
- Offers versatile control options for diverse applications.
- Ideal for high-performance and accurate operations.
8 Wire
- Multiple wiring options for advanced control setups.
- Operates in both unipolar and bipolar modes.
- Perfect for applications requiring precise and flexible control.
Based on Control Systems
Stepper motors can be controlled through open-loop or closed-loop systems, offering flexibility for both simple and precise applications.
Open-loop
- No feedback system, controlled by step pulses.
- Simple and cost-effective for basic applications.
- Suitable for light-load, low-precision tasks.
Closed-loop
- Integrates feedback for accurate control of position and speed.
- Provides higher efficiency, reduces overheating and vibration.
- Ideal for high-torque, variable-load, and precision applications.
Featured Products






Common Applications
Stepper motors are used in applications requiring precise movements, such as CNC machines, robotics, HVAC systems, automotive, industrial equipment, and more.
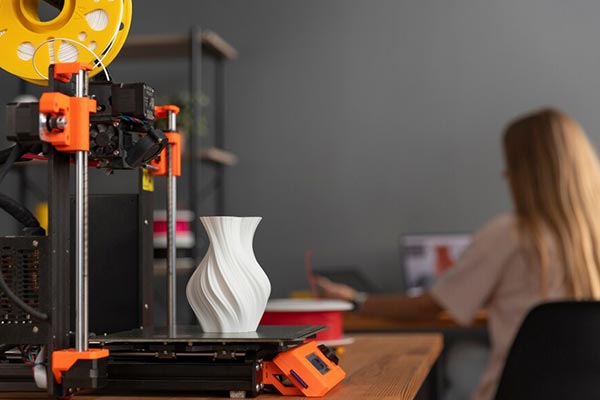

3D Printer
- Used in 3D printers to drive precise movements, enabling accurate layer-by-layer construction and high-resolution object creation.
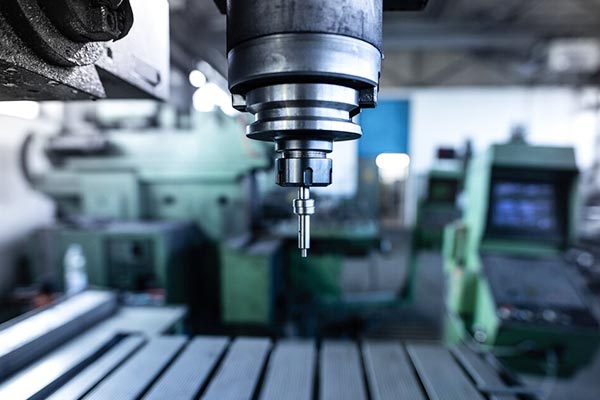

CNC Machine
- In CNC routers, it precisely controls the movement of cutting tools, ensuring efficient and accurate machining for complex designs.
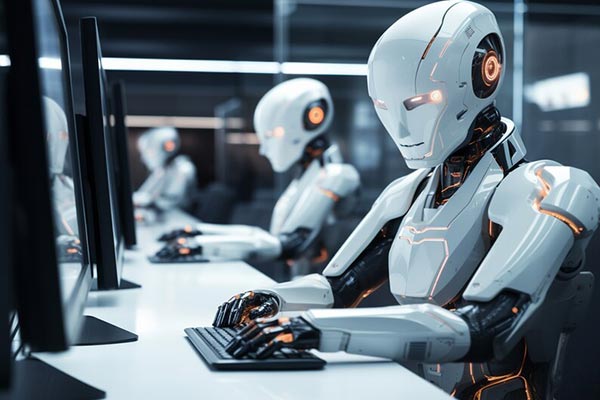

Robotic
- Drives robotic arms and legs, providing precise control for tasks such as assembly, welding, and movement in automated systems.
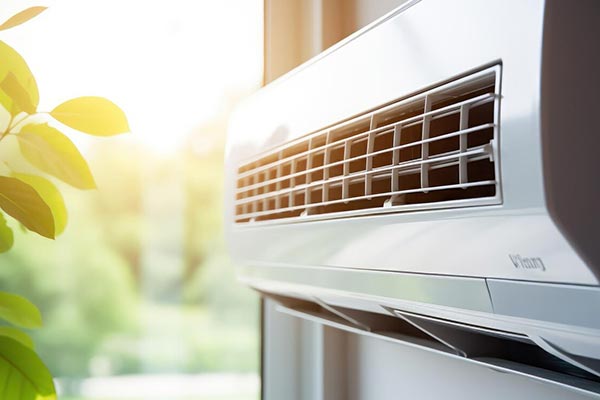

HVAC
- Regulates fan speeds and damper positions, ensuring proper airflow, energy efficiency, and temperature control within HVAC systems.

Car
- Used to control automotive gauges, offering smooth and precise movements for displaying information like speed, fuel level, and engine status.

CD Drive
- In CD drives, it positions the laser and rotates the disc, allowing for accurate reading and data retrieval from optical media.

Conveyor Systems
- Control the movement of belts and items, ensuring smooth and reliable transport of materials in manufacturing and logistics.

Textile Machine
- In sewing machines, it controls needle and thread movement, ensuring consistent stitching and precision during high-speed textile production.

