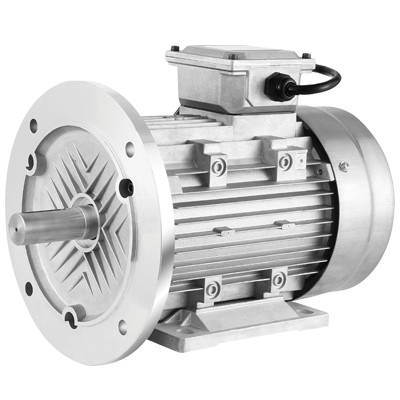
Professionally Customize Automobile Motor
Recommended Supporting Suppliers for
Global First-tier OEMs
Industrial Product Supporting Capacity
Low Noise,High Quality,Safety, Low Energy Consumption
Industry Innovations
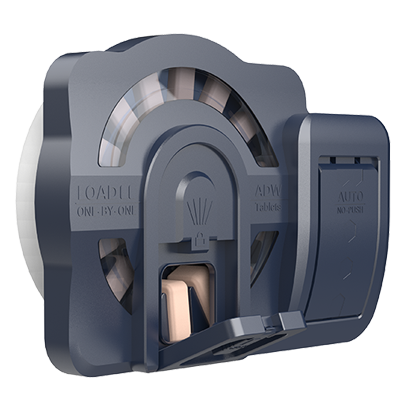
Dishwasher Dispenser Series
- Intelligent tips for a comfortable home life
- Reliable dispensing for the ultimate experience
- Highly adaptable to meet the diverse needs of users
- Modular design for easy operation
New Products for Automotive Air Conditioning Applications
Automotive Air Damper / Motorised Air Vent Actuator
- Miniaturised solutions, Smaller size, Meet the demand for lightweight automotive products
- Domestic chip, Stable supply, Maintain a certain price advantage
- Consistent size and performance, Can replace the imported product programme
Founded in 1993
Stock code 300660

Qualification

Professional customization
Annual production:200 million motors+

500+
World famous brand partner
Products and Applications
-
Home Appliance Market
Committed to providing innovative solutions for the global home appliance industry
- Leading brand in global air conditioning sweep motor market
- A global leader in washing machine drainage systems
- Global Refrigerator lce Water System Solution Provider
Home Appliance Market
Committed to providing innovative solutions for the global home appliance industry
- Customer Cases




- Specific Classfication
 Air Conditioner
Air Conditioner Refrigerator
Refrigerator Washing Machine
Washing Machine Kitchen & Bathroom
Kitchen & Bathroom Small Home Appliances
Small Home Appliances
-
Auto Parts
Provide motor and mechatronic components for automobiles
- Product advantages of stepper motors for HUD
- Large-scale automotive water pump production capacity
- Automotive air conditioning system solution capabilities
Auto Parts
Provide motor and mechatronic components for automobiles
- Customer Cases




- Specific Classfication
 Air Conditioning System
Air Conditioning System Thermal Management
Thermal Management Intelligent Driving
Intelligent Driving Intake & Exhaust System
Intake & Exhaust System Body Control
Body Control Braking System
Braking System
-
Industrial Control
Provide cost-effective motor and component products in the industrial field
- First-tier brand suppliers in the valve control market
- Domestic security monitoring head enterprise supplier
- Multiple series of products meet different application scenarios
Industrial Control
Provide cost-effective motor and component products in the industrial field
- Customer Cases




- Specific Classfication
 Valve Control
Valve Control OA Finances
OA Finances Garden Tools
Garden Tools Industrial Equipment
Industrial Equipment Security Monitoring
Security Monitoring Robot
Robot
-
Sports Health
Provide high-quality motors for sports equipment and medical equipment industries
- High-end sports equipment main drive motor supplier
- First-tier brand suppliers in the medical device industry
- Ability to provide solutions such as smart furniture
Sports Health
Provide high-quality motors for sports equipment and medical equipment industries
- Customer Cases




- Specific Classfication
 Sports Equipment
Sports Equipment Medical Instruments
Medical Instruments Game Entertainment
Game Entertainment Smart Home
Smart Home
Outer Diameter 20-50mm
Outer Diameter 6.5-60mm
Outer Diameter 35-60mm
Motors for Valve Control
Full Range of Brushless Types
Various Options Available
DC/AC Programme
Washing Machine Drain Pumps
Automotive Heat Management Pumps
Motors for Valve Control
New Products
- The industrial motor on the market is mainly AC high energy consumption, and the application of permanent magnet motor is less.
Rare Earth Removal Efficient
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor
More efficient and energy-saving than same-priced asynchronous motor.
Trending for Industrial Motor Development
- High efficiency, energy saving and green development
- Intelligent and integration
Self-developed Stator Soft Magnetic Material
- Strong plasticity, simple manufacturing process
- Energy saving, environmental protection, high strength
Self-developed Magnetic Rotor Material
- High dimensional stability
- Double permeability design, improve the motor full frequency high efficiency band
Integrated Design
- Small size, light weight
- Intelligent, low noise
- Domestic dishwasher penetration rate is low, the market demand has continued to increase in recent years, the market outlook is large.
Industry Innovative
Intelligent Dishwasher Dispenser
Multiple options for different types of detergents.
Dishwasher Development Trend
- High-end functional requirements
- Wider market prospects for embedded / single-use
- Dishwasher detergents towards integration and liquidisation

Highly Adaptable
- Four options to choose from
- Meets most of the dishwasher detergent dispensing needs on the market
Reliable Detergent Dispensing
- Reliable, active pushing out of the dishwasher block
- Liquid filling pump with good liquid viscosity adaptability
Modular Design
- Modular design, simple structure
- Plug-in installation of the dosing pump
- Increasing demand for automotive comfort, automotive air conditioning market trends towards electrification and intelligence.
Automotive Air Damper / Motorised Air Vent Actuator
Miniaturised solutions for lightweight requirements.
Automotive Air Conditioning Air Vents Market Trends
- Automotive air conditioning air vents electrification, intelligence
- Large air outlet area, wide-angle wind sweeping
- Require high efficiency and good stability of air vents

Product Lightweighting
- Miniaturised solutions with smaller dimensions
- Meet the demand for lightweight automotive products
Stable Supply
- Domestic chip, can provide stable supply
- Maintain a certain price advantage
Substitute for Imported Products
- Maintain the same size and performance
- There can be a substitute for imported products programme
Client Cooperation

Providing you with a full range of CUSTOMISED SERVICES

Relying on the application advantages and customer base in the drainage system of washing machines, Leili continues to meet the needs of new projects of customers and provide customized solutions for the functional requirements of high-end washing machines. After years of research and development, the automatic feeding system for washing machines has been mass-produced by customers such as Little Swan and Whirlpool.

The application of Leili motor in refrigerator products is mainly synchronous motor. In recent years, the customer’s demand for refrigerator ice-making function, Leili motor and the customer close communication, collaborative research and development of refrigerator ice and water system components, for the customer to produce high-end refrigerator to provide assistance. At present, the refrigerator component products have been developed in series for different application scenarios of different customers such as Whirlpool, Midea and GE.
News Center
On January 8, 2026, Leili Overseas Manufacturing Base – Leili Malaysia Co., Ltd. – held a grand opening ceremony in the Selangor Industrial Park, Malaysia. Mr. Su Da, General Manager of Jiangsu Leili, led his executive team to the site, witnessing this historic moment together with local representatives, partners, and distinguished guests. Leili Motors’ intelligent manufacturing base in Malaysia is a crucial step in Leili’s globalization strategy. It not only carries the mission of producing millions of high-end motors annually but also embodies Leili’s determination to cultivate the Southeast Asian market deeply.

In his speech, General Manager Su Da stated, “We chose Malaysia as Leili’s overseas base because of this vibrant land. It boasts a diverse cultural blend, a thriving industrial ecosystem, and unique geographical advantages. Located in the heart of Southeast Asia, it offers an open and inclusive business environment, efficient and pragmatic policy support, a mature and complete industrial chain, diligent and intelligent local talent, and a stable and harmonious social environment. Investing in and building a factory in Malaysia is a significant step in our globalization strategy, aligning perfectly with our strategy of ‘deeply cultivating Asia and connecting with the world.’ This will become another frontier for Leili, following our Vietnam base, to serve customers in the Asia-Pacific and North American markets, and a crucial cornerstone of our global layout.”
Regarding the industry, Leili Malaysia will leverage its automated production lines, intelligent warehouses, and precision manufacturing technology to promote the upgrading of the local industrial chain, driving the coordinated development of upstream and downstream local suppliers, and helping to create a more competitive manufacturing cluster in Malaysia.
Regarding society, the Leili Malaysia factory will directly create more than 200 jobs, with over 85% of them for local recruitment. It will also gradually establish industry-academia-research cooperation models with local governments and universities, contributing to the industrial talent ecosystem and providing employees with professional and systematic training and a conducive work environment, helping them grow into high-quality blue-collar workers, technical experts, and managers.

Regarding the environment, the transformation and upgrading of future factories will utilize photovoltaic power generation and low-emission processes to achieve “carbon-neutral” operations, demonstrating the concept of sustainable development through practical actions and aligning with Malaysia’s “National Low Carbon Transition Blueprint 2050.” Standing at this new starting point and looking towards a new future, at this historical juncture of the 52nd anniversary of diplomatic relations between China and Malaysia, Raley is committed to using this factory as a new starting point, upholding its original aspirations, pioneering and striving forward, and working hand in hand with its Malaysian partners to jointly write a new chapter of “joint consultation, joint construction, and shared benefits”!
LEILI is excited to participate in the upcoming 137th Canton Fair, scheduled from April 15th to April 19th at the Canton Fair Complex, No.382, Yuejiang Zhong Road, Guangzhou. As a global leader in motion control and motor solutions, LEILI is excited to meet customers, partners, and visitors from around the world during this premier international trade event.
This spring session of the Canton Fair, known as China’s largest and most comprehensive trade fair, presents an invaluable opportunity for industry professionals to explore the latest trends, forge new connections, and discover cutting-edge products. At LEILI, we are proud to be part of this dynamic platform once again.
Visit LEILI at Booth No. 19.2E35-36, 19.2F13-14
We warmly welcome all attendees to visit us at our booth No. 19.2E35-36 and 19.2F13-14, where we will showcase our full portfolio of innovative motor products and intelligent drive systems. From precision micro motors to integrated motion control solutions, LEILI’s products are widely applied in smart home appliances, medical equipment, industrial automation, and automotive systems.
Visitors will have the chance to:
- Examine the introduction of new products with cutting-edge features and increased effectiveness.
- Experience live demonstrations of our motor solutions in action
- Engage with our professional team to discuss custom solutions for your application needs
- Discover LEILI’s latest R&D advancements in brushless motors, stepper motors, servo systems, and more
With over two decades of expertise and a strong commitment to innovation, LEILI continues to lead the way in delivering reliable, energy-efficient, and intelligent motor solutions to clients around the globe.
What to Expect at LEILI’s Booth
Our booth will highlight LEILI’s core technologies and product advantages. You’ll see:
- High-performance BLDC motors designed for smooth operation and high torque output
- Stepper motors and gear motors developed for precise positioning and quiet operation
- Advanced servo drive systems offering superior control for industrial automation
- Customized motor assemblies tailored to meet specific customer requirements
Our engineering and sales teams will be on-site, ready to provide in-depth technical support and one-on-one consultation. Whether you’re seeking a standard model or a fully customized solution, LEILI offers the flexibility and expertise to support your unique project.
Let’s Connect and Innovate Together
The Canton Fair is more than an exhibition — it’s a global meeting point for ideas, technology, and partnerships. At LEILI, we believe in the power of collaboration to create smarter and more sustainable motion solutions. We look forward to sharing our vision and learning from your insights.
Mark your calendar:
📅 Date: April 15–19, 2025
📍 Venue: Canton Fair Complex, No.382 Yuejiang Zhong Road, Guangzhou
🧭 Booth: 19.2E35-36, 19.2F13-14
Welcome to our booth — let’s shape the future of motion together!

A brushless direct current (DC) motor, also known as a synchronous electric motor, is driven by DC electricity instead of a mechanical commutation system. Brushless DC motors have high efficiency and reliability, help lower acoustic noise, and offer dynamic response, high speed range, and long durability, which are among the key features expected to leverage the brushless DC motor market growth.
Request For Sample Copy of this Research Report:https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/insight/request-sample/1438
The higher efficiency of brushless DC motors in comparison with other induction or magnetic motors is driving the growth of the brushless DC motors market. Brushless DC motors are more efficient than their brushed DC counterparts, as it is associated with lower mechanical wear outs, thus lowering maintenance costs.
Brushless motor operates at low temperatures, require minimum maintenance, are thermally resistant, and remove any threat of sparks. This, in turn, has increased the demand for brushless motors over other types. Integration of sensor-less controls in brushless DC motors helps boost the durability and reliability of the product, in turn decreases the number of mechanical misalignment and electrical connections and reduces the weight and size of the product. The demand for the sensor-less controls from the industrial machinery has increased considerably due to its low cost and robust motor drives.
Among end users, the industrial automation equipment segment held the largest market share in the brushless DC motors market due to the growing demand for hybrid and electric cars. According to the International Energy Agency, in 2016, electric car sales were over 750 thousand worldwide. The consumer goods segment is rapidly growing due to increasing demand for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) technology, which in turn is increasing the demand for brushless DC motors.
Asia Pacific held the large brushless DC motors market share due to the rising production of electric cars and increasing demand for consumer electronics. According to the International Energy Agency, in 2016, China held the largest market share in the electric cars market, accounting for over 40% of the global electric cars sold.
The market in North America is expected to witness the fastest growth due to the growing demand for extremely sophisticated medical devices. For example, the development of positive airway pressure (PAP) breathing apparatus for the treatment of sleep apnea. This device, which helps patients in breathing also employs a brushless DC motor to power the blower fan.
Key players operating in the brushless DC motors market include Johnson Electric, Ametek, MinebeaMitsumi Inc., Allied Motion Technologies Inc., Maxon Motor AG, Emerson Electric Corporation, ABB, Nidec Corporation, and ARC Systems.
For More Information: https://www.coherentmarketinsights.com/ongoing-insight/brushless-dc-motors-market-1438
Electrification is transforming sectors such as transportation, robotics, aerospace, and energy. Across all these sectors, one requirement remains constant: achieving higher performance while reducing weight, volume, and energy consumption.
Unlike traditional radial motors, axial motors are designed to deliver high torque density in a flat, compact form factor. Their unique geometry allows engineers to rethink system integration, eliminate mechanical complexity, and reduce overall system mass.
Understanding Lightweight Electrification
Lightweight electrification refers to the integration of electric power and motion systems that minimize mass while maintaining or improving performance. Weight reduction is not merely a structural concern—it directly impacts efficiency, energy consumption, thermal behavior, and system lifespan.
In electric vehicles, lighter systems translate into longer driving range and improved acceleration. In aerospace and drones, reduced weight enables higher payloads and extended flight times. In robotics and automation, lightweight drives improve responsiveness, safety, and precision.
Motors play a central role in this equation. As one of the heaviest and most energy-intensive components in an electrified system, motor selection significantly influences overall system performance. Axial motors address many of the challenges faced by traditional motor architectures in lightweight applications.

Axial Motor Design Principles
Axial motors differ fundamentally from radial motors in magnetic flux orientation and structural layout. In a radial motor, magnetic flux extends outward from rotor to stator. In an axial motor, the magnetic flux travels parallel to the motor shaft, allowing torque to be generated across a large effective radius.
This design offers several inherent advantages:
- Short axial length, resulting in a flat, pancake-like structure
- Large active diameter, increasing torque leverage
- Efficient use of magnetic materials, improving power density
- Flexible rotor-stator configurations, including single-rotor/single-stator and multi-rotor designs
Because torque is proportional to force multiplied by radius, the larger effective radius of axial motors enables higher torque output without increasing motor mass. This feature is especially crucial in space- and weight-constrained applications.
Why Weight Matters in Electrified Systems
Weight reduction in electrified systems yields multiple cascading benefits:
Energy Efficiency
Reduced mass lowers inertia, requiring less energy for acceleration and braking.
Thermal Performance
Lightweight designs often simplify cooling paths, reducing thermal bottlenecks and improving reliability.
System Integration
Compact motors enable tighter integration with gearboxes, wheels, or driven components, eliminating couplings and reducing mechanical losses.
Cost and Sustainability
Less material usage lowers raw material costs and environmental impact, especially critical for high-volume electrification.
Axial motors directly contribute to all these areas by enabling high performance in a smaller, lighter package.
Torque Density and Power-to-Weight Advantage
One of the defining metrics in lightweight electrification is torque density—torque output per unit mass or volume. Axial motors consistently outperform many radial motor designs in this regard.
Axial Motor vs. Radial Motor – Key Performance Comparison
| Parameter | Axial Motor | Radial Motor |
| Torque Density | Very High | Moderate |
| Axial Length | Short | Long |
| Power-to-Weight Ratio | High | Medium |
| Cooling Efficiency | High (surface exposure) | Moderate |
| Integration Flexibility | Excellent | Limited |
| Mechanical Complexity | Low | Medium |
The flat geometry of axial motors allows them to generate higher torque at lower rotational speeds, often eliminating the need for reduction gears. Removing gearboxes not only reduces weight but also improves efficiency and system reliability.
Role of Axial Motors in Electric Mobility
Electric Vehicles (EVs)
In electric vehicles, weight is directly linked to driving range, battery size, and cost. Axial motors enable:
- Compact e-axle designs
- In-wheel motor integration
- Reduced drivetrain mass
- Higher efficiency at partial loads
By delivering high torque at low speeds, axial motors reduce reliance on multi-stage transmissions. This simplification leads to lighter drivetrains and improved vehicle packaging flexibility.
Micro-Mobility and Two-Wheelers
Electric scooters, bikes, and small motorcycles require efficient, compact motors. Axial motors are well-suited for hub-drive or mid-drive configurations where space constraints are severe.
Their thin profile allows designers to integrate motors without compromising aesthetics or ergonomics, while their high torque output supports smooth acceleration and hill-climbing capability.
Lightweight Electrification in Robotics and Automation
Robotic systems prioritize precision, responsiveness, and safety. Even small weight changes impact dynamics in collaborative robots and platforms.
Axial motors contribute to lightweight robotics by:
- Reducing joint mass, improving acceleration and deceleration
- Enabling direct-drive architectures, eliminating backlash
- Enhancing torque control and motion smoothness
- Improving energy efficiency during continuous operation
In humanoid robots, autonomous mobile robots, and exoskeletons, axial motors help achieve a balance between strength and agility. Their compact form allows actuators to be placed closer to joints, improving kinematic performance and reducing structural stress.
Aerospace, Drones, and Advanced Mobility
Weight sensitivity is most extreme in aerospace and unmanned aerial systems. In these applications, axial motors play a crucial role in enabling electrification where traditional motors are too heavy or inefficient.
Key benefits include:
- Higher thrust-to-weight ratios
- Improved thermal dissipation in low-pressure environments
- Compact integration into wings, propellers, or distributed propulsion systems
eVTOL aircraft depend on several lightweight motors spread across the airframe. Axial motors support this architecture by combining high power density with scalable modular designs.
Thermal Management and Cooling Advantages
Thermal performance is a limiting factor in high-power-density systems. Axial motors offer inherent cooling advantages due to their geometry:
- Large surface area exposed to ambient air
- Short heat conduction paths from windings to housing
- Compatibility with liquid or air cooling systems
Efficient thermal management allows axial motors to operate at higher continuous power levels without increasing mass. This capability is essential for lightweight electrification, where oversized motors for thermal margin are not acceptable.

Materials and Manufacturing Considerations
Advances in materials science and manufacturing technologies have accelerated the adoption of axial motors. Lightweight electrification benefits from:
- High-energy-density permanent magnets
- Thin electrical steel laminations to reduce core losses
- Advanced composite housings
- Advanced manufacturing methods like laser cutting and robotic winding
Design Factors Supporting Lightweight Axial Motors
| Design Factor | Contribution to Lightweight Electrification |
| High-Grade Magnets | Increased torque without added mass |
| Thin Laminations | Reduced iron loss and heat generation |
| Direct-Drive Architecture | Eliminates gearbox weight |
| Modular Rotor-Stator Design | Scalable power without redesign |
| Integrated Cooling Channels | Maintains power density |
While manufacturing axial motors can be more complex than radial motors, ongoing improvements in automation and tooling are reducing cost barriers and improving consistency.
System-Level Impact of Axial Motors
The true value of axial motors in lightweight electrification lies at the system level rather than the component level. When integrated thoughtfully, they enable:
- Smaller batteries due to higher efficiency
- Reduced structural reinforcement due to lower mass
- Simplified mechanical layouts
- Improved reliability through fewer moving parts
These benefits compound across the entire system, making axial motors a strategic choice rather than a simple motor substitution.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their advantages, axial motors are not universally ideal. Challenges include:
- Higher initial design complexity
- Specialized manufacturing requirements
- Sensitivity to air-gap tolerances
- Cost considerations for low-volume production
However, in applications where weight and efficiency are critical, these challenges are often outweighed by performance gains.
Future Outlook: Axial Motors and the Next Phase of Electrification
As electrification expands into new domains—such as aviation, space systems, wearable robotics, and advanced industrial automation—the demand for lightweight, high-performance motors will continue to grow.
Axial motors are expected to play an increasingly prominent role due to:
- Continued improvements in materials and cooling
- Greater standardization and scalability
- Integration with power electronics and control systems
- Alignment with sustainability and energy efficiency goals
In many next-generation electrified platforms, axial motors will not merely replace radial motors—they will enable entirely new architectures that were previously impractical.
Conclusion
Lightweight electrification is no longer an optional design goal; it is a defining requirement across modern engineering disciplines. Axial motors address this requirement by offering exceptional torque density, compact form factors, and system-level efficiency advantages.
By reducing weight, simplifying drivetrains, and improving thermal performance, axial motors empower designers to push the boundaries of what electrified systems can achieve. From electric vehicles and robotics to aerospace and advanced mobility, their role in lightweight electrification solutions is both transformative and enduring.
As technology continues to evolve, axial motors are poised to become a cornerstone of efficient, high-performance, and sustainable electrified systems worldwide.
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors (PMSMs) have found widespread use across various industries due to their remarkable performance characteristics. These motors, known for their high efficiency, reliability, and precise control, have become indispensable in applications that demand exacting standards. Among the most critical of these applications are CNC machines and medical devices. This article explores the role of PMSMs in these high-precision fields, examining their benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
The Basics of PMSMs
The key feature of PMSMs is their ability to maintain synchronization with the supply current, making them highly efficient and responsive. PMSMs offer advantages over other motors, including:
- High Efficiency: The use of permanent magnets reduces energy losses, making PMSMs more energy-efficient.
- Precision Control: The synchronization between the stator and rotor ensures high accuracy in speed and position control.
- Compact Design: PMSMs have a high power-to-weight ratio, allowing for compact and lightweight motor designs.
- Low Maintenance: PMSMs require minimal maintenance due to the absence of brushes or slip rings that wear out.

The Role of PMSMs in CNC Machines
CNC machines are vital in manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, and metalworking, requiring precise movement for accurate cutting, milling, and drilling. PMSMs have become a preferred choice for CNC applications due to their superior control and precision.
Precision and Accuracy
CNC machines rely heavily on precise motion control to achieve the desired end product. In these machines, PMSMs provide the required high-precision rotation of the spindle and axes, ensuring that parts are cut with minimal deviation from the design specifications. PMSMs’ high torque density and smooth operation ensure CNC accuracy. The motor’s ability to maintain synchronization with the controller allows for real-time adjustments, enabling ultra-precise machining of parts.
High Torque at Low Speeds
One of the significant advantages of PMSMs in CNC machines is their ability to deliver high torque at low speeds. This is essential for applications such as milling, where the motor needs to generate substantial torque to cut through materials while maintaining slow and controlled movement. PMSMs excel in such scenarios, ensuring that the CNC machine operates smoothly and without vibration, which is crucial for maintaining dimensional accuracy.
Enhanced Control and Efficiency
CNC machines often work with intricate patterns and complex designs, requiring precise and dynamic control of motion. PMSMs, when paired with advanced control systems, offer exceptional dynamic performance. The feedback loop between the motor and controller allows for constant monitoring and adjustment, ensuring that the motor’s position, speed, and torque are optimized throughout the process.
The efficiency of PMSMs reduces energy consumption, making CNC machines cost-effective for high-precision tasks. The reduced heat generation and lower energy losses contribute to longer machine lifespans and reduced operating costs.
Table 1: PMSM Advantages in CNC Machines
| Feature | Benefit |
| High Efficiency | Reduced energy use and costs. |
| Precision Control | Precise speed and position control |
| High Torque at Low Speeds | Enables slow, controlled cutting with minimal vibration |
| Compact Design | Space-saving motor design suitable for compact CNC machines |
| Low Maintenance | Low wear, less downtime |
PMSMs in Medical Devices
In the medical field, precision is paramount. Whether it’s a diagnostic tool, surgical robot, or a medical pump, the performance of medical devices depends on the motor’s ability to provide accurate and reliable motion. PMSMs are increasingly being adopted in these applications due to their precision, reliability, and the ability to operate efficiently in demanding environments.
Surgical Robots and Medical Robotics
Surgical robots represent one of the most advanced applications of PMSMs. These robots, used in minimally invasive surgeries, require precise and smooth movement to perform delicate procedures. PMSMs are ideal for these tasks because of their ability to deliver fine motion control, essential for tasks such as tissue cutting, suturing, and even robotic-assisted organ transplants.
The use of PMSMs in surgical robots allows for high levels of precision in a confined space, which is often required during procedures like endoscopy or laparoscopic surgeries. Moreover, PMSMs provide the necessary torque to handle complex surgical tools, ensuring that the robot can perform intricate movements without compromising the patient’s safety.
Diagnostic Equipment
In diagnostic applications such as MRI machines, CT scanners, and ultrasound devices, PMSMs play a crucial role in maintaining the precision required for accurate imaging. For example, MRI machines rely on powerful magnetic fields and precise motion control to obtain clear and detailed images. PMSMs are used to control the position of the scanner components, ensuring that the system operates with the necessary precision and reliability.
Similarly, in other diagnostic devices, PMSMs are used to power pumps, motors, and actuators, ensuring that these devices deliver accurate results consistently.
Medical Pumps
Medical pumps deliver precise medication, fluids, or nutrients; PMSMs are essential in infusion, insulin, and dialysis pumps for accuracy and reliability.
The accurate and efficient motion provided by PMSMs ensures that these pumps operate consistently, delivering the right amount of medication or fluid at the right time.

PMSM Advantages in Medical Devices
| Feature | Benefit |
| High Precision | Essential for performing delicate tasks such as surgery |
| Low Noise and Vibration | Ideal for sensitive medical environments |
| Compact and Lightweight | Ideal for small, portable medical device integration. |
| Reliability and Durability | Guarantees continuous operation in vital healthcare environments. |
| Energy Efficiency | Low power use, lowering operational costs in healthcare. |
Challenges and Limitations of PMSMs in High-Precision Applications
While PMSMs offer numerous advantages, their application in high-precision industries like CNC machines and medical devices is not without challenges.
Cost
A major challenge of PMSMs is their high cost. Permanent magnets, particularly those made from rare-earth materials, can be expensive, which makes PMSMs costlier than other motor types, such as induction motors. This can be a limiting factor for small businesses or medical startups looking to implement high-precision technologies on a budget.
Heat Management
Although PMSMs are generally more efficient than traditional motors, they can still generate heat, especially when operating at high power levels or in enclosed environments. As such, proper heat management systems, including ventilation and cooling mechanisms, must be in place to ensure that the motor operates within safe temperature limits.
Control Complexity
High-precision applications require advanced motor control systems. These systems must be highly sophisticated, incorporating feedback loops, sensors, and algorithms to manage the motor’s speed, position, and torque. Control system complexity can increase costs and timelines.
The Future of PMSMs in High-Precision Applications
The future of PMSMs in high-precision applications looks promising. As technology advances, the development of more affordable and efficient PMSMs is expected to drive their adoption across a broader range of industries. In CNC machines, we can expect to see even more compact and efficient motors, contributing to the miniaturization of machine tools and improvements in manufacturing processes.
In the medical field, PMSMs will continue to play a pivotal role in the evolution of surgical robotics and diagnostic tools, providing greater precision and reliability in increasingly complex medical procedures.
Moreover, ongoing research into the use of advanced materials for permanent magnets, along with the development of novel cooling and control technologies, will help address current challenges such as cost and heat management. As PMSMs become more affordable and efficient, their role in high-precision applications is expected to expand, providing even greater performance and reliability.
Conclusion
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motors have proven themselves to be a cornerstone in high-precision applications, from CNC machines to medical devices. Their high efficiency, precision, and low maintenance requirements make them an ideal choice for industries where performance and accuracy are critical. Despite the challenges associated with cost, heat management, and control complexity, the future of PMSMs in high-precision applications looks bright. As technology continues to advance, PMSMs will remain at the forefront of innovation, driving progress in manufacturing, healthcare, and beyond.
Incorporating PMSMs into these applications has already led to significant improvements in efficiency, precision, and reliability, making them an indispensable tool in modern technology. As new breakthroughs emerge, PMSMs will undoubtedly play a central role in the next generation of high-precision systems.
Efficient airflow management is a cornerstone in industrial applications, HVAC systems, cleanrooms, data centers, and many other engineered environments. The fan market has evolved tremendously over the years, with more sophisticated solutions delivering higher performance, lower energy consumption, and superior control. Among the most significant advancements are Electronically Commutated (EC) backward-curved centrifugal fans—often touted as the new benchmark in airflow technology.
In contrast to traditional fan types—such as axial fans, forward-curved centrifugal fans, and standard induction-motor-driven backward-curved fans—EC backward-curved centrifugal fans provide several advantages. However, understanding where these advantages apply most, and when traditional fans still serve effectively, is crucial for designers, engineers, and procurement specialists.

Fan Technology Overview
Before diving into direct comparisons, it’s useful to summarize the technologies under discussion.
Electronically Commutated (EC) Backward-Curved Centrifugal Fans
EC fans use a brushless DC motor with integrated electronics that combine the motor and variable speed drive into one compact assembly. The impeller in a backward curved configuration has blades that curve against the direction of wheel rotation.
Key characteristics:
- Combines motor and drive electronics in one unit
- Delivers high efficiency across various operating conditions
- Minimizes electrical losses for enhanced performance
- Offers precise control with variable speed capabilities
- Low noise compared to conventional motors
Traditional Fan Types
Traditional fans can be grouped into a few broad categories:
- Axial Fans – Air moves parallel to the axis, offering simplicity and cost-effectiveness, but limited pressure.
- Forward-Curved Centrifugal Fans – Impeller blades curve with rotation, making them ideal for low-pressure systems, such as HVAC.
- Backward-Curved Centrifugal Fans (Standard) – Blades curve against rotation, higher pressure capability, often driven by AC induction motors.
- Propeller Fans – A subtype of axial fan for low-pressure, high-volume applications (e.g., ventilation).
- Tubeaxial and Vaneaxial Fans – Axial fans with duct adapters for HVAC air movement.

Fundamental Performance and Efficiency Comparison
Performance and efficiency are critical when selecting a fan. They determine energy consumption, space requirements, and utility cost over the lifecycle.
Aerodynamic Performance
Backward-curved centrifugal fans generate higher static pressures, making them ideal for ducted systems with significant airflow resistance.
Below provides a concise comparison of various fan types in terms of static pressure capability, airflow range, and typical applications.
Performance Comparison of Fan Types
| Feature / Metric | EC Backward Curved Centrifugal | Standard Backward Curved Centrifugal | Forward Curved Centrifugal | Axial / Propeller Fans |
| Static Pressure Capability | High | High | Moderate | Low |
| Airflow Range | Moderate to High | Moderate to High | Moderate | High |
| Efficiency | Very High | Moderate | Low to Moderate | Moderate |
| Energy Control / Variable Speed | Excellent (integrated) | Good (external VFD) | Fair | Good (external VFD) |
| Noise Levels | Low | Moderate | Moderate to High | High |
| Typical Applications | HVAC, Data Centers, Cleanrooms, Industrial | HVAC, Industrial | HVAC, Low-Pressure Duct Systems | Ventilation, Cooling |
| Cost | Higher upfront | Moderate | Lower | Lowest |
Efficiency and Energy Use
EC backward-curved fans utilize permanent magnets and integrated drive electronics which greatly reduce electrical losses common in induction motors. This translates to up to 50%+ savings in energy use compared to traditional AC motor fans in variable load applications.
Traditional fans typically use AC induction motors. When paired with Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs), they can achieve some level of speed control but still suffer from additional conversion losses and control limitations.
System Control and Integration
One of the key advantages of EC fans is their integrated control logic, which is designed to seamlessly connect with:
- Analog signals (0-10V, 4-20mA)
- Digital communication (Modbus, BACnet)
- Feedback sensors (pressure, temperature, humidity)
This capability enables:
- Airflow optimization based on real-time demand
- Reduced energy waste during off-peak conditions
- Integration with building automation systems
By contrast, traditional fans require external drives and controllers to achieve similar control, increasing complexity and installation costs.
Durability, Maintenance, and Lifecycle Considerations
A fan’s total cost of ownership is heavily influenced by its reliability and maintenance needs.
Motor Durability
- EC Fans: Use brushless motors with electronic commutation. Less mechanical wear, lower heat generation, and typically longer life if operated within rated conditions.
- AC Induction Motor Fans: Simple and rugged but constitute wear in bearings and belts (if present). They often require periodic inspections and maintenance.
Bearing and Impeller Wear
Backward-curved centrifugal fans generally produce less turbulence at the inlet and discharge, reducing mechanical stress and extending operational life.
Maintenance Needs and Downtime
Maintenance activities like lubrication, belt replacement, and drive servicing are more frequent with traditional fan assemblies, especially in demanding environments.
EC fans simplify maintenance schedules due to fewer wearable components and integrated diagnostics that can alert operators to service needs.
Cost Analysis: Upfront vs. Lifecycle
Upfront Costs
- EC Backward-Curved Fans: Higher upfront cost due to integrated electronics and advanced motor technology.
- Traditional Fans: Lower initial cost, especially simple axial or forward-curved fans.
However, upfront costs do not reflect true value.
Operating Costs
EC fans run more efficiently and adaptively, resulting in:
- Lower electricity bills
- Reduced HVAC loads
- Lower peak demand charges
- Extended system life
For facilities operating multiple fans continuously (e.g., data centers, commercial HVAC), energy savings often pay back the premium on EC fans within 1–3 years.
Lifecycle Cost Comparison
Table 2 below outlines typical cost categories and how EC backward curved fans compare with traditional fans over a 10-year operational life.
Lifecycle Cost Comparison (10-year Estimated)
| Cost Category | EC Backward Curved Fan | Traditional Fan (Induction Motor Driven) |
| Initial Purchase | High | Low to Moderate |
| Installation & Commissioning | Moderate | Moderate |
| Energy Consumption | Lowest | High |
| Control System Costs | Integrated (lower) | External (higher) |
| Maintenance | Low | Moderate to High |
| Downtime & Service Interruptions | Low | Higher |
| Total 10-Year Cost | Competitive / Lower | Higher |
| Return on Investment (ROI) | Good | Moderate |
Noise and Environmental Impact
Noise and vibration are often overlooked factors but critical in comfort-sensitive environments like offices, hospitals, and residential HVAC.
Noise Levels
- EC Backward-Curved Fans: Quieter operation due to smoother motor control and optimized impeller design.
- Traditional Fans: Can generate more noise, especially at higher speeds or under fluctuating loads.
Lower noise also correlates with reduced vibration and structural load, which benefits equipment longevity.
Environmental Considerations
- Energy Efficiency: EC fans reduce energy use and carbon footprint.
- Material Use: EC fans are typically more compact, reducing material consumption.
Recyclability: Many components are recyclable, but electronic modules may complicate end-of-life recycling if not properly managed.
Practical Installation and Application Considerations
HVAC Systems
EC backward-curved centrifugal fans are particularly effective in modern HVAC units because:
- Airflow can be modulated automatically based on demand
- Static pressure compensation is excellent for ducted systems
- Lower sound levels improve occupant comfort
Traditional fans may still be suitable for simple ventilation or applications where control needs are minimal.
Industrial Process Applications
Industrial processes requiring precise airflow, such as drying systems, ovens, and manufacturing lines, benefit from:
- Stable pressure delivery
- Variable airflow control
- High efficiency at partial loads
Data Centers and Cleanrooms
These environments demand reliability and precise control. EC backward-curved fans deliver:
- Consistent airflow under varying thermal loads
- Lower energy draw (critical in high-density compute environments)
- Integration with environmental monitoring systems
- Traditional fans, even high-quality ones, often lag in control and efficiency.
When Traditional Fans Still Make Sense
Despite the advantages of EC backward-curved fans, traditional fans retain relevance in certain contexts.
Low Initial Budget Constraints
Project budgets with tight upfront capital may favor simpler traditional fans where advanced controls are not essential.
Simple Ventilation Needs
Applications focused on basic ventilation (e.g., warehouses, agricultural ventilation) might not benefit significantly from advanced flow control.
Retrofit Scenarios with Minimal Integration Needs
Older systems without modern control infrastructure may not justify the complexity of EC fan installation if the goal is simple replacement rather than system upgrade.
8. Future Trends and Technology Outlook
Fan technology continues evolving. Current trends include:
- Smart IoT integration – fans connected via networks for real-time monitoring
- Predictive maintenance – sensors relay data to anticipate failures
- Advanced materials – composites, coatings to reduce weight and improve performance
- Higher efficiency standards – regulatory push for energy performance (e.g., IE5 equivalents)
EC fan technology aligns well with these trends, making it a future-ready solution compared to traditional counterparts.
Summary and Key Takeaways
EC backward-curved centrifugal fans represent a significant technological step forward in airflow management, combining high efficiency, precise control, low noise, and reduced lifecycle costs. When compared with traditional fan types, especially those driven by AC induction motors, the benefits are particularly notable in:
- Energy efficiency and control
- Lifecycle cost savings
- Integration with automation systems
- Operational flexibility
However, traditional fan types still have roles where simplicity, low initial cost, or basic performance is sufficient.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Fan Type
Selecting the right fan technology depends on:
- Performance requirements – pressure, airflow, environmental conditions
- Control needs – demand response, automation
- Budget priorities – upfront vs. lifecycle cost
- Noise and comfort considerations
- Integration with existing systems
For most modern commercial and industrial applications, EC backward-curved centrifugal fans offer a compelling combination of performance, efficiency, and control. Traditional fans remain relevant for straightforward, low-pressure ventilation or cost-constrained projects.
A careful evaluation against the criteria above ensures the most effective and economical choice for your airflow system.
In today’s energy-conscious world, efficiency is paramount in every industry, and one of the technologies contributing to this is the EC fan (Electronically Commutated fan). These fans combine the efficiency of direct current (DC) motors with the convenience of alternating current (AC) power sources.
With applications ranging from industrial ventilation to HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, EC fans are rapidly becoming the go-to solution for those looking to reduce energy consumption without compromising performance.

What is an EC Fan?
An EC fan is a type of fan that uses an Electronically Commutated (EC) motor. Unlike traditional AC or DC fans, EC fans feature a brushless permanent magnet motor with integrated electronics that adjust the fan’s speed based on demand. This integration of the motor and controller offers superior energy efficiency and control.
Key Features of EC Fans:
- Energy Efficiency: EC fans are more energy-efficient than traditional fans due to the advanced control of speed and power.
- Quiet Operation: They provide quieter operation by reducing vibration and motor noise.
- Variable Speed Control: EC fans automatically adjust their speed to match the required airflow, optimizing power consumption.
- High Efficiency at Partial Loads: Unlike conventional fans that operate at full power all the time, EC fans use only the energy required for the given load, leading to significant energy savings.
How Do EC Fans Work?
EC fans use a brushless DC motor (BLDC) that combines the best of both AC and DC systems. The key component is the built-in electronic controller that adjusts the speed and power supply. Unlike standard AC motors, which run at a constant speed, EC fans can vary their speed according to the system’s demands, providing a more efficient performance.
The fan operates by:
- Transforming AC power into DC power through an integrated rectifier.
- Controlling the fan’s speed through an integrated electronic controller, which modulates the DC power supply.
- Optimizing airflow by adjusting the motor’s performance based on the load or airflow requirements.
This combination of motor and electronics leads to a closed-loop system that provides improved control over the fan’s performance, ultimately delivering enhanced energy efficiency.
Advantages of EC Fans
Energy Efficiency
A major benefit of EC fans is their energy efficiency, as traditional AC fans run at full speed constantly, regardless of airflow demand. In contrast, EC fans adjust their speed to match the required airflow, ensuring that the motor runs at optimal efficiency.
Variable Speed Control
EC fans feature variable speed control, which allows for dynamic adjustments based on real-time airflow requirements. This flexibility reduces energy consumption during low-demand periods and ensures the fan operates at peak efficiency during high-demand times.
Reduced Operating Costs
By improving efficiency and reducing energy consumption, EC fans help to lower overall operating costs. This is especially useful for applications requiring continuous or prolonged fan operation, like HVAC and cooling systems.
Longer Lifespan
The brushless nature of EC motors eliminates wear and tear associated with traditional brushed motors. This leads to increased durability and reduced maintenance, enhancing reliability and lowering long-term costs.
Quiet Operation
EC fans also offer significantly quieter operation. The fan speed can be controlled more precisely, reducing the noise levels often associated with traditional fans. This is particularly important in environments such as offices, hospitals, and residential buildings, where noise levels need to be minimized.
Environmentally Friendly
EC fans consume less energy, reducing electricity use and lowering greenhouse gas emissions, which helps decrease your operation’s carbon footprint and supports environmental sustainability.
Applications of EC Fans
EC fans are versatile and widely used in various industries including:
HVAC Systems
EC fans optimize airflow, enhance energy efficiency, and boost overall system performance in HVAC applications. These fans can be found in air handling units (AHUs), ventilation systems, and cooling towers, where their energy-efficient operation is critical.
Industrial Ventilation
EC fans are commonly utilized for ventilation in industrial environments. Whether it’s maintaining air quality in factories or providing cooling for equipment, EC fans can ensure that the air volume is controlled efficiently while saving energy.
Data Centers
Data centers need accurate temperature and airflow control to avoid overheating. EC fans vary speed based on heat load, enhancing cooling system performance and energy efficiency.
Refrigeration Systems
In refrigeration, EC fans are used to maintain airflow and temperature control. The variable speed control ensures that the fan operates efficiently, reducing the energy consumed in refrigeration units, which often run continuously.
Appliances
EC fans are increasingly being incorporated into home appliances like air conditioners, heat pumps, and extractor fans, where they provide quieter and more efficient operation compared to traditional fan systems.
Automotive Cooling
EC fans are also used in automotive applications, especially in the cooling systems of electric vehicles (EVs). They regulate battery and motor temperatures, enhancing vehicle performance and longevity.

Types of EC Fans
Axial EC Fans
Axial EC fans move air along the fan’s axis, making them suitable for applications requiring high airflow at low pressure, such as HVAC, ventilation, and industrial cooling.
Centrifugal EC Fans
Centrifugal EC fans generate higher pressure than axial fans and are typically used in systems requiring higher airflow resistance, such as air handling units and ducted ventilation systems.
Backward Curved EC Fans
Backward curved EC fans are designed for high-efficiency applications, providing a good balance between airflow and pressure. They are used in applications where space is limited but high efficiency is required, such as in HVAC systems and ventilation equipment.
Forward Curved EC Fans
Forward curved EC fans offer higher airflow but at lower pressure. These fans are ideal for applications prioritizing air movement over pressure, like small exhaust systems.
Choosing the Right EC Fan
When selecting an EC fan for your application, there are several factors to consider. The right fan will depend on the specific needs of your system, such as airflow volume, pressure, and energy consumption.
Key Factors to Consider:
| Factor | Description |
| Airflow Requirements | Ensure the fan can deliver the required volume of air (CFM or m³/h). |
| System Resistance | Consider the static pressure the fan can overcome, depending on the system’s ductwork. |
| Energy Efficiency | Look for fans with integrated electronics to adjust speed based on load. |
| Noise Levels | Choose fans that offer quieter operation for noise-sensitive environments. |
| Speed Control | Determine if variable speed control is necessary for your application. |
EC fans are a revolutionary step forward in fan technology, offering energy-efficient, reliable, and quiet operation across various industries. By understanding the benefits, applications, and types of EC fans, you can make a more informed decision on which fan is right for your needs, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
With their ability to adapt to changing airflow requirements, EC fans are poised to play a key role in future energy-efficient systems. As energy costs rise and environmental concerns grow, adopting EC fan technology is a wise choice for anyone looking to optimize their systems while reducing operational costs.




